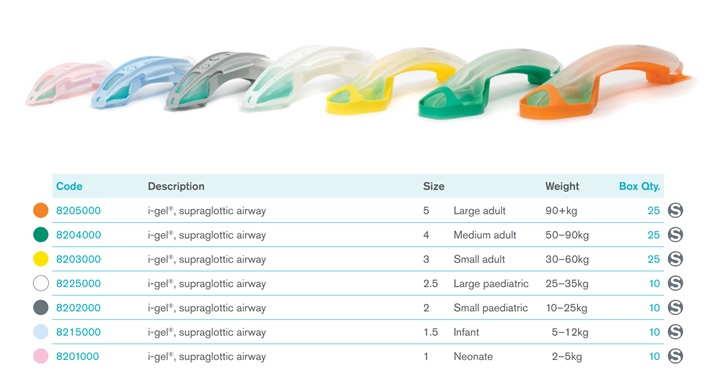
I-GEL SUPRAGLOTTIC AIRWAY 38.01
EMT
The i-gel® supraglottic airway is to be utilized as an adjunct to providing ventilation to a patient with respiratory arrest.
The i-gel® replaces the King LT airway, and the CombiTube airway. The user must be trained in its use.
Indications
- Ventilation with a BVM (with OPA/NPA in place) is inadequate.
- Endotracheal intubation is unsuccessful or unavailable.
- Patient is unconscious without a gag reflex.
- No history of esophageal foreign body or caustic ingestion
Contraindications
- Obstructive lesions below the glottis
- Trismus, limited mouth opening, pharyngo-perilaryngeal abscess, trauma or mass
- Conscious or semi-conscious patient with intact gag reflex
-
Warnings and Notes
- Do not use peak pressure of ventilation to exceed 40 cm H2O
- Do not use excessive force to insert the device
- Use caution in patients with fragile dental work
- Use care to avoid the introduction of lubricant in or near the ventilatory openings
-
Procedure
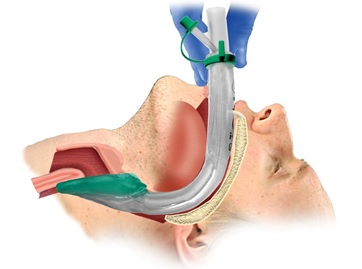
- Grasp the lubricated i-gel® firmly along the bite block (tube portion). Position the device so that the i-gel® cuff outlet is facing towards the chin of the patient.
- NOTE: be sure that there is only a thin layer of lubricant on the end of the i-gel® to avoid blowing it into the lungs with bagging.
- Suction the upper airway PRIOR to insertion as needed.
- The patient should be in the “sniffing” position. If cervical injury is suspected, use the modified jaw thrust instead of any flexion of the neck.
- Introduce the leading soft tip into the mouth of the patient towards the hard palate.
- Glide the device down and back along the hard palate with a continuous but gentle push until definitive resistance is felt.
- Do not apply excessive force on the device during insertion. It is not necessary to insert fingers or thumb into the oral cavity of the patient during insertion. If there is resistance during insertion, a “jaw thrust” and/or slight rotation of the device is recommended.
- After proper insertion, the tip of the device should be located into the upper esophageal opening and the cuff should be located into the laryngeal framework. The incisors should be resting on the integrated bite block.
Post Placement
- Auscultate breath sounds, check for chest rise, confirm placement with ETCO2 monitoring and SpO2 monitoring.
- attach SpO2 monitor and capnometer
- ETCO2 goal is 35-40 mmHg
- Secure the tube
- In prolonged respiratory support (>20 minutes), place OG tube (ie, 12F suction catheter) in the side port and advance to appropriate position, apply suction to decompress the stomach
Removal
- Have suction ready. Suction oral cavity before removal if indicated
- Carefully remove the i-gel® airway with gentle, but firm, traction. Suction as needed.
- Insert an oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal adjunct as needed
- Continue ventilations with a BVM or place non-rebreather mask.
- Document time of removal and ongoing vital signs
Paramedic
- Sedate as necessary
- Consider definitive airway placement
- Endotracheal intubation may be accomplished utilizing the i-gel® tube with Bougie introducer